Entrance Announcement
MICTE 2080
2080 Magh 07
User:Saroj Neupane Lesson Plan 6: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created blank page) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="column-count: 2; column-gap: 20px;"> | |||
'''Subject :''' Computer Science | |||
'''Period:''' 3rd | |||
'''Topic:''' Machine Learning and its Applications | |||
'''School:''' ABC School | |||
'''Class:''' 10 | |||
'''Unit:''' Seven | |||
'''Time:''' 15 min | |||
'''No. of Students:''' 20 | |||
</div> | |||
== Specific Objectives == | |||
* At the end of the class students will be able to understand key concepts, types of ML, and real-world applications. | |||
== Teaching Materials == | |||
* Whiteboard and markers or a digital presentation tool | |||
* Projector or screen (if using digital presentation) | |||
== Teaching Learning Activities (10 minutes) == | |||
* Start with a question: "How do you think computers can learn and make decisions without being explicitly programmed?" Encourage students to share their thoughts. | |||
[[File:Applications-of-machine-learning.png|thumb|Applications of ML]] | |||
* Provide a concise definition: "Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence where computers learn patterns from data to make predictions or decisions without explicit programming." | |||
* Arthur Samuel first used the term "machine learning" in 1959. | |||
* Introduce key types of machine learning: | |||
# Supervised Learning: Learning from labeled data with input-output pairs. | |||
# Unsupervised Learning: Learning from unlabeled data to find patterns. | |||
# Reinforcement Learning: Learning through trial and error with a reward-based system. | |||
* Discuss fundamental concepts: | |||
# Training Data: The dataset used to train the machine learning model. | |||
# Algorithms: Mathematical models that learn patterns from data. | |||
# Features: Input variables used by the model to make predictions. | |||
# Predictions: The output generated by the machine learning model. | |||
[[File:Ho ML works.png|thumb|How Machine Learning works?]] | |||
* Describe how machine learning works? | |||
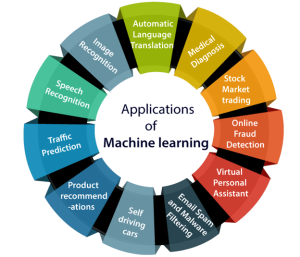
* Discuss on applications of Machine Learning. | |||
== Case Study or Example (2 minutes): == | |||
* Share a brief case study or example that illustrates how machine learning is applied in a specific industry or scenario. Use visuals or a short video clip if available. | |||
== Conclusion and Q&A (1 minute) == | |||
* Summarize the key points discussed in the lesson. | |||
* Open the floor for questions from students. | |||
== Assessment == | |||
A. Multiple choice questions | |||
<quiz> | |||
{What is machine Learning? | |||
|type="()"} | |||
-A type of computer virus | |||
+A branch of artificial intelligence | |||
-A programming language | |||
-A hardware component | |||
{Which term is used to describe the dataset used to train a machine learning model? | |||
|type="()"} | |||
-Test Data | |||
-Input Data | |||
+Training Data | |||
-Output Data | |||
{In Supervised Learning, what is the role of labeled data? | |||
|type="()"} | |||
-To test the model's performance | |||
+To train the model | |||
-To validate the model | |||
-To ignore the model | |||
{Which of the following is a real-world application of Machine Learning? | |||
|type="()"} | |||
-Building a website | |||
-Sorting files on a computer | |||
+Fraud detection in financial transactions | |||
-Sending emails | |||
</quiz> | |||
B. What are the applications of Machine learning? | |||
[[Category:Lesson Plan]] | |||
__notoc__ | |||
== Optional Activity (if time allows) == | |||
Conclude with a brief interactive activity, such as asking students to brainstorm potential applications of machine learning in their daily lives. | |||
Revision as of 06:31, 1 December 2023
Subject : Computer Science
Period: 3rd
Topic: Machine Learning and its Applications
School: ABC School
Class: 10
Unit: Seven
Time: 15 min
No. of Students: 20
Specific Objectives
- At the end of the class students will be able to understand key concepts, types of ML, and real-world applications.
Teaching Materials
- Whiteboard and markers or a digital presentation tool
- Projector or screen (if using digital presentation)
Teaching Learning Activities (10 minutes)
- Start with a question: "How do you think computers can learn and make decisions without being explicitly programmed?" Encourage students to share their thoughts.
- Provide a concise definition: "Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence where computers learn patterns from data to make predictions or decisions without explicit programming."
- Arthur Samuel first used the term "machine learning" in 1959.
- Introduce key types of machine learning:
- Supervised Learning: Learning from labeled data with input-output pairs.
- Unsupervised Learning: Learning from unlabeled data to find patterns.
- Reinforcement Learning: Learning through trial and error with a reward-based system.
- Discuss fundamental concepts:
- Training Data: The dataset used to train the machine learning model.
- Algorithms: Mathematical models that learn patterns from data.
- Features: Input variables used by the model to make predictions.
- Predictions: The output generated by the machine learning model.
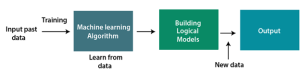
- Describe how machine learning works?
- Discuss on applications of Machine Learning.
Case Study or Example (2 minutes):
- Share a brief case study or example that illustrates how machine learning is applied in a specific industry or scenario. Use visuals or a short video clip if available.
Conclusion and Q&A (1 minute)
- Summarize the key points discussed in the lesson.
- Open the floor for questions from students.
Assessment
A. Multiple choice questions
B. What are the applications of Machine learning?
Optional Activity (if time allows)
Conclude with a brief interactive activity, such as asking students to brainstorm potential applications of machine learning in their daily lives.